Ultrasound Guided Injections
Joint injections are a minimally invasive treatment for relieving pain caused by inflammatory joint conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, tendonitis, bursitis and gout. To reduce pain and inflammation from these conditions, medications such as corticosteroids and hyaluronic-acid preparations are sometimes injected into the problem joint. The medications affect only the targeted areas, and usually do not cause side effects. Joint injections are administered under local anesthesia, and cause only brief, mild discomfort.
To ensure precise administration of, and effective results from, joint injections, they are often performed under ultrasound guidance. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the internal structures of the body; no radiation is involved and there are no side effects. As with traditional injections, ultrasound-guided injections are made with standard needles and syringes. The difference is that, during ultrasound, a probe attached to a monitor is placed against the skin in the target area; this gives the physician an internal view of the joint to be injected. The physician watches the monitor as she or he places the needle into the joint, ensuring precise placement.
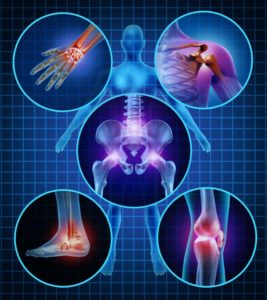
Joint injections can be used to relieve pain in the following areas:
- Knee
- Shoulder
- Ankle
- Elbow
- Wrist
- Thumb
- Hip
Unless they have joint infections or allergies to the medications used, most people are candidates for ultrasound-guided joint injections, which generally take between 15 and 30 minutes to perform.
Steroid Injections For Arthritis
Arthritis is a condition that causes, pain, swelling and stiffness in the joints. Treatment for arthritis may vary, but the main goal is to reduce inflammation and pain. Most patients may try several different treatment options before finding a method that works best for their individual condition. Steroid injections are an advanced treatment option for patients with arthritis and other sources of joint pain, that have not responded well to other treatments such as exercise and oral medications. These injections deliver relief directly to the source of the pain and are considered safe for nearly all patients.
Most steroid injections provide immediate anti-inflammatory relief by being injected directly into the affected joint. These injections are an effective method of treatment to reduce the swelling of tendons and ease pressure on the nerve. A steroid medication such as cortisone, is injected directly into the inflamed area and works by minimizing the body’s reaction to inflammation. As the inflammation decreases, the pressure is relieved, therefore causing pain and discomfort to subside. As a result, patients experience a decrease in symptoms such as pain, swelling, numbness or stiffness. Symptoms may subside within a few days and the results of the injection may last for a few weeks or up to a few months.
Carpal Tunnel Injections
The carpal tunnel is a narrow, fibrous passage in the wrist that protects the median nerve, which runs down the length of arm and through the wrist into the hand. It controls some hand movement, and sensation in the thumb, index and middle fingers, and half of the ring finger. Irritation or compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel can cause tingling and numbness in the fingers, as well as pain in the arm, a condition known as carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
CTS is linked to, among other conditions, wrist injuries and diabetes, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. And although no link has conclusively been shown to exist, certain repetitive motion activities seem to cause CTS.
An effective treatment for CTS is corticosteroid injection, which reduces the swelling of tendons, easing pressure on the median nerve. Injected directly into the inflamed area, the corticosteroid works by minimizing the body’s reaction to inflammation. Pain, numbness, weakness and tingling typically subside within a few days of the patient’s being injected. The relief provided by the injections lasts for a few weeks to a few months.
Tarsal Tunnel Injections
Tarsal tunnel injections are a treatment for tarsal tunnel syndrome, also known as posterior tibial neuralgia, a condition characterized by chronic pain in the foot and ankle. Tarsal tunnel syndrome is caused by abnormal compression on the tibial nerve, a branch of the sciatic nerve that supplies sensation to the foot. Although tarsal tunnel syndrome is not a serious condition, the pain it causes can be acute. Patients may also experience sensations of burning, cramping, tingling or numbness. Fortunately, tarsal tunnel injections can provide welcome relief from these symptoms.
Tarsal tunnel injections, which contain corticosteroids and a local anesthetic, are administered in the doctor’s office. The medications are injected directly into the tarsal tunnel, as close to the aggravated nerve as possible. A topical anesthetic is normally used on the skin to reduce the discomfort of the injection itself. Tarsal tunnel injections are an effective remedy for tarsal tunnel syndrome.The local anesthetic produces immediate relief by numbing the affected area, while the corticosteroid provides effective long-term pain relief by reducing inflammation for an extended period.
Tarsal tunnel injections may provide weeks, or even months, of relief from discomfort due to tarsal tunnel syndrome. If they are successful in relieving pain, they may be repeated. Because such injections may have serious side effects, they should not be administered more often than every 5 weeks and usually not more than 3 or 4 times a year.
Bursal Sac Injections
A bursal sac is filled with fluid that provides a cushion between muscles/tendons and bones to decrease friction and irritation. There are bursal sacs around most of the body’s joints. When a bursal sac gets infected or inflamed, it can lead to a painful condition called “bursitis.” Although often caused by repetitive movement or overuse of a joint during sports or intense physical activity, bursitis can also result from injury, or arthritis of a joint.
The most common symptoms of bursitis are pain, stiffness, swelling and tenderness, usually in the joints of the elbow, shoulder, hip, knee or ankle. The heel and Achilles tendon can also be affected. Pain, which can develop gradually or be sudden and severe, may be accompanied by decreased mobility of the joint.
If conservative treatment methods are unsuccessful in treating the pain and discomfort caused by bursitis, bursal sac injections can be an effective way of reducing inflammation and diminishing pain. Anti-inflammatory steroid medication is injected directly into the bursal sac; as inflammation decreases, pain and discomfort subside, often for a few weeks or months. In some cases, one injection may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms.